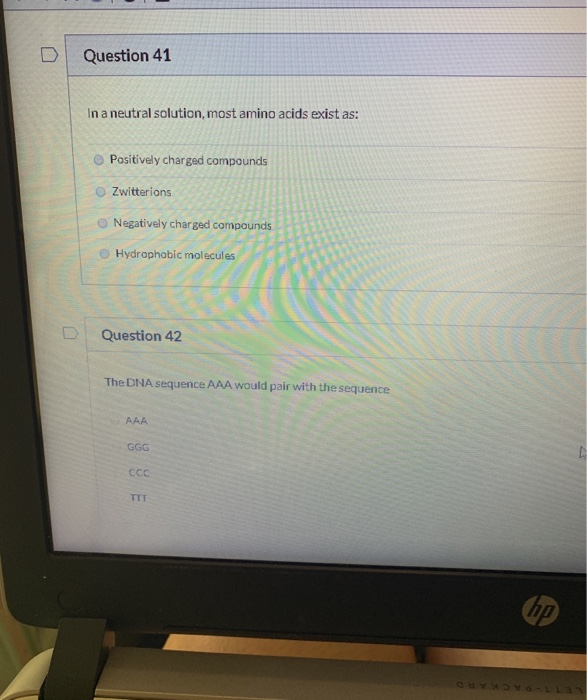
In a Neutral Solution Most Amino Acids Exist as
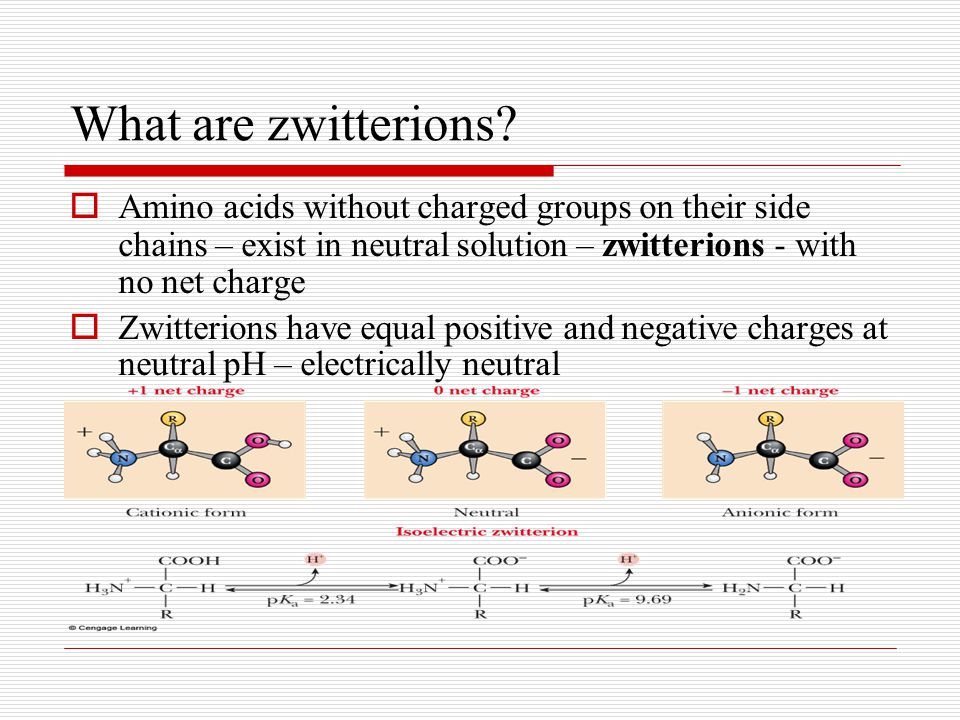
The neutral zwitterion is the usual form amino acids exist in solution. The amino acids generally form diprotic or triprotic systems in aqueous solution.
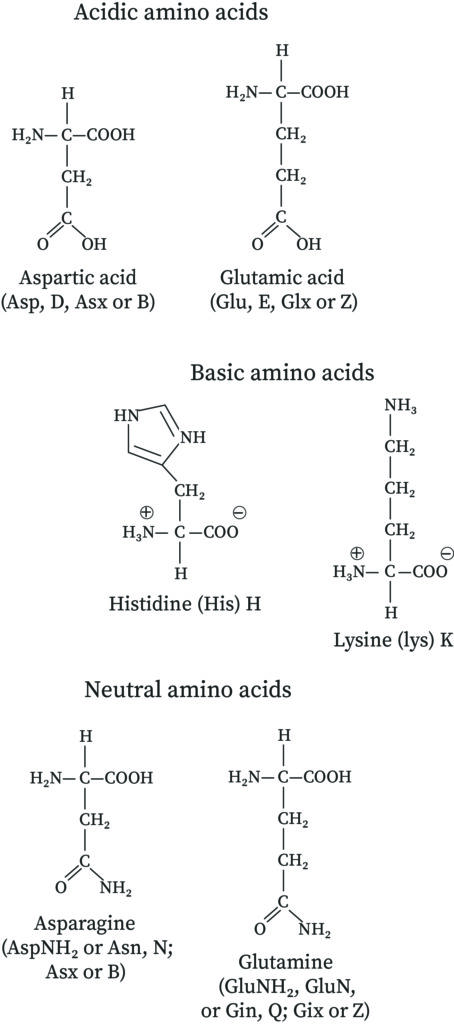
There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral pH.
. In a neutral solution most amino acids exist as. Using glycine as an example and given that the pKa of the carboxyl group is 23 and that of the ammonium group is 96 predict the predominant form of the molecule at pH 1 7 and 12. If the amino acid structure contains two acid groups and one amine group there is a net acid.
They are very soluble in water. PH of that solution will be 02 07 12 O 14 QUESTION 4 Most amino acids exist in the L-form because All Amino acids are R. In a neutral solution most amino acids exist as.
All of this suggests that they exist as ionic species. In this situation the acidic and basic groups on the amino acids will be ionized. This pH isoelectric point pI.
C negatively charged compounds. Are zwitterions always neutral. Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia which is a base.
This parallels the behavior of a diprotic acid. Amino acids that contain only the α amino and α carboxyl groups which act as Brønsted-Lowry acid-base conjugate pairs somewhere within the normal aqueous pH range meaning that the pK a of the acidic form of the pair lies between 0 and 14 effectively form a diprotic system with. This dipolar ion is a zwitterion so choiceB is the correct answer.
The structure of a zwitterion is shown below. Zwitterion is the most biologically relevant form of amino acids as it is their most abundant form in living organisms. Same is true for the amino groups pKb is at pH 115 for arginine.
A positively charged compounds. In a neutral solution most amino acids exist as. Amino acids with polar R groups that form hydrogen bonds to water are classified as hydrophilic water-loving.
They are synthesized in the zwitterionic form and are. I made a short table describing the protonation states of the two groups. Most amino acids exist as zwitterions dipolar ions at pH 7.
In a neutral solution most amino acids exist as. AMINO ACIDS-OO NH 3 COO S--Aspartic Acid Asp D S--Glutamine Gln Q S--Valine Val V S--Tryptophan Trp W S--Phenylalanine. The carboxyl group is negatively charged in a solution much higher than the pKa of the carboxyl group which is pH 248 for arginine.
C negatively charged compounds. So at pH 95 the ratio of the positively charged amino group to a neutral amino group is 1001 at the pKb it would be 5050. Because of the charges.
The standard amino acids are therefore classified on the basis of these R groups. B Most amino acids except the acidic and basic amino acids have two sites for protonation. At neutral pH the carboxylic acid will be deprotonated -COO- and the amine group will remain protonated -NH3.
Since proteins are biological molecules they are usually found in a neutral solution that is buffered at pH 70 to 74. Most of these amino acids differ only in the nature of the R substituent. These are arginine Arg lysine Lys and histidine His.
An amino acid has this ability because at a certain pH value different for each amino acid nearly all the amino acid molecules exist as zwitterions. The remaining amino acids have. For more information you can read.
In a neutral solution most amino acids exist as. Steric Hindrance is minimum in this form. Amino acids with nonpolar substituents are said to be hydrophobic water-hating.
Amino acids are crystalline solids with very high melting points in excess of 200 o C. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen H ion and the amino acid becomes positively charged. The carboxylic acid and the amine group.
QUESTION 2 The net neutral form of glycine is given by O NH2CH2COOH NH3CH2COOH NH2CH2COO- O NH3CH2COO QUESTION 3 If the concentration of OH-ions in a solution is 10-2 M. With two dissociation steps controlled by two acidity constants K 1 and K 2. At neutral pH amino acids exist as dipolar ions.
At neutral pH values they exist as zwitterions with the carboxyl group deprotonated and. 23 rows If the side chain contains an acid functional group the whole amino acid produces an acidic solution. Normally an amino acid produces a nearly neutral solution since the acid group and the basic amine group on the root amino acid neutralize each other in the zwitterion.
Their pKas are high enough that they tend to bind protons gaining a. Amino Acids as Acids Bases and Buffers. A positively charged compounds.
PH Carboxyl group exists as Amino group exists as Net charge 2 C O O H neutral N H X 3 X positively charged 1 2 C O O X negatively charged N H X 3 X positively charged 0 9 C O O X negatively charged N H X 2 neutral 1. Note that all amino acids are at one point electrically neutral at some pH value. Amino acids in solution at neutral pH usually exist in this form when the amino group is protonated NH 3 and the carbonyl group dissociated COO.
Two amino acids that contain sulfur atoms are. O pH pKa Equal amounts of protonated and deprotonated species exist if pH is LESS than the pKa of a particular group that. Depending on the pH there are two other forms an anion and a cation.
Amino Acids And Peptides Ppt Download
Solved Di Question 41 In A Neutral Solution Most Amino Chegg Com
No comments for "In a Neutral Solution Most Amino Acids Exist as"
Post a Comment